
Cockroach Management
Cockroach management is the process of controlling or eliminating cockroach populations, which can spread diseases and trigger allergies in humans. Cockroaches are a common household pest found in many parts of the world, and their presence can be a nuisance as well as a health hazard.
Cockroach management typically involves a combination of techniques, including sanitation, exclusion, and chemical treatment. Sanitation measures involve cleaning up food spills and removing sources of water, as cockroaches require moisture to survive. Exclusion involves sealing cracks and crevices to prevent cockroaches from entering buildings.
Chemical treatment involves the use of insecticides to kill cockroaches and their eggs, and can include both conventional insecticides and newer, less toxic treatments such as baits and insect growth regulators.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an effective approach to cockroach management that combines multiple techniques to achieve long-term control while minimizing the use of chemicals. IPM may include the use of traps, monitoring devices, and education and outreach to prevent cockroach infestations from occurring in the first place.
The goal of cockroach management is to eliminate cockroach infestations and prevent their return, while minimizing the impact on human health and the environment. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the biology and behavior of cockroaches, as well as the specific conditions of the affected area.

Fly Management
Fly management is the process of controlling or eliminating populations of flies, which can spread diseases and contaminate food and other surfaces. Flies are a common pest found in many parts of the world, and their presence can be a nuisance as well as a health hazard.
Fly management typically involves a combination of techniques, including sanitation, exclusion, and chemical treatment. Sanitation measures involve removing sources of food and water, as well as cleaning up animal waste and garbage, which can attract flies. Exclusion involves sealing gaps and cracks to prevent flies from entering buildings.
Chemical treatment involves the use of insecticides to kill adult flies and their larvae, and can include both conventional insecticides and newer, less toxic treatments such as baits and microbial insecticides.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an effective approach to fly management that combines multiple techniques to achieve long-term control while minimizing the use of chemicals. IPM may include the use of traps, screening, and education and outreach to prevent fly infestations from occurring in the first place.
The goal of fly management is to eliminate fly infestations and prevent their return, while minimizing the impact on human health and the environment. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the biology and behavior of flies, as well as the specific conditions of the affected area.
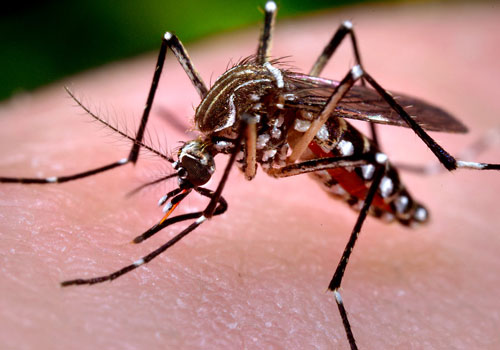
Mosquito Management
Mosquito management is the process of controlling or eliminating mosquito populations, which can transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus. Mosquitoes are a common pest found in many parts of the world, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions, and their populations can be controlled through a variety of methods.
Mosquito management typically involves a combination of techniques, including environmental management, source reduction, and insecticide application. Environmental management involves modifying the environment to reduce mosquito breeding sites, such as removing standing water and improving drainage. Source reduction involves identifying and eliminating mosquito breeding sites, such as empty containers or pools of water.
Insecticide application is another important tool for mosquito management, and can involve the use of larvicides and adulticides to target different stages of the mosquito life cycle. Larvicides are used to kill mosquito larvae before they develop into adults, while adulticides are used to kill adult mosquitoes.
Integrated mosquito management (IMM) is a holistic approach to mosquito management that combines multiple techniques to achieve effective control of mosquito populations while minimizing environmental impact. IMM includes a range of approaches, such as biological control, community education, and surveillance, in addition to the methods mentioned above. The goal of mosquito management is to reduce the risk of mosquito-borne disease transmission and promote public health.

Termite and Wood Borer Management
Termite and wood borer management is the process of controlling or eliminating infestations of termites and wood borers, which can cause damage to wooden structures and furniture. Termites and wood borers are insects that feed on wood and cellulose-containing materials, and their infestations can lead to structural damage and economic loss.
Termite and wood borer management typically involves a combination of techniques, including inspection, monitoring, and treatment. Inspection involves identifying the type of pest present and determining the extent of the infestation, as well as identifying conditions that may be conducive to pest activity.
Monitoring involves regular inspections to detect pest activity and determine the effectiveness of control measures. Treatment may involve the use of chemicals such as insecticides, physical barriers such as mesh screens or sealants, or cultural practices such as removing infested wood.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach to termite and wood borer management that combines multiple techniques to achieve long-term control while minimizing the use of chemicals. IPM may include preventive measures such as building design and construction techniques that discourage pest activity, as well as cultural practices such as regular inspection and maintenance.
The goal of termite and wood borer management is to protect wooden structures and furniture from damage, while minimizing the impact on human health and the environment. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the biology and behavior of the pests, as well as the specific conditions of the affected area.

Bed Bug Management
Termite and wood borer management is the process of controlling or eliminating infestations of termites and wood borers, which can cause damage to wooden structures and furniture. Termites and wood borers are insects that feed on wood and cellulose-containing materials, and their infestations can lead to structural damage and economic loss.
Termite and wood borer management typically involves a combination of techniques, including inspection, monitoring, and treatment. Inspection involves identifying the type of pest present and determining the extent of the infestation, as well as identifying conditions that may be conducive to pest activity.
Monitoring involves regular inspections to detect pest activity and determine the effectiveness of control measures. Treatment may involve the use of chemicals such as insecticides, physical barriers such as mesh screens or sealants, or cultural practices such as removing infested wood.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach to termite and wood borer management that combines multiple techniques to achieve long-term control while minimizing the use of chemicals. IPM may include preventive measures such as building design and construction techniques that discourage pest activity, as well as cultural practices such as regular inspection and maintenance.
The goal of termite and wood borer management is to protect wooden structures and furniture from damage, while minimizing the impact on human health and the environment. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the biology and behavior of the pests, as well as the specific conditions of the affected area.

Rat Management
Rat management is the process of controlling or eliminating rat populations, which can cause damage to property, spread disease, and pose a threat to human health. Rats are a common pest found in urban and rural areas around the world, and they can cause a range of problems, including damage to buildings, food contamination, and the spread of diseases such as leptospirosis and hantavirus.
Rat management involves several steps, including identification of the type of rat present, assessment of the level of infestation, and determination of the most appropriate control measures. Control measures can include the use of traps, rodenticides, and exclusion methods to prevent rats from entering buildings.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a common approach to rat management, which involves a combination of techniques to reduce or eliminate rat populations. IPM includes preventive measures such as sanitation and exclusion, as well as the use of non-toxic control methods such as traps and baits. The goal of rat management is to reduce rat populations to a level where they no longer pose a threat to human health or property.

Lizard Management
Lizards are common pests in houses, factories & building areas. There are several different types of lizards that naturally occur in and around houses, building, and factories and nearby hot places. They may be targeted as a pest according to season or geographical regions. Lizards are pest simply by their presence indoors. They do not live or infest indoor areas but come from surrounding while most people do not like lizards or get frightened by their presence on interior walls and counters parts of premises. These animals are not harmful. They will not bite people or pests generally.
Lizards are inactive primarily during day and night time. They move indoors during the early evening or early morning in search of insects that are attracted to lights. Lizards feed primarily on insects and spiders. They especially prefer ants as their food. They are solitary animal (reptiles) but they may occur in large numbers where there is an abundant vegetation & moist conditions. Matting occurs in the spring & eggs are laid. Soon after the eggs are hatched in summer young lizards take about 2 years to become adult and start roaming. The young ones are recognized by their small sign of short tail present.
Mode of Treatment This treatment would be carried out by directing the recommended pesticides towards the lizards, ant their hideouts & killing them. Spraying of target specific pesticides will be done on electric wires, meter rooms, bathroom, windows, tunnels, cracks & crevices, and conduits to avoid their presence and elimination.
Bad effect of Lizard Lizard is very harmful to us if it gets consumed with food that quite happens and we used to hear such news also. That can cause a sure death in maximum cases. It is very dangerous if we take any kind of food in which a lizard has fallen and got rotten in it.

Disinfection
Disinfection involves the destruction of microorganisms, but not usually spores, on inanimate surfaces or objects. Disinfection is not sterilization. Sterilization describes a process that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life, including spores. Disinfection methods can involve the use of physical (e.g., heat or ultraviolet light) or chemical (e.g., disinfectants) processes to reduce, inactivate, or destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
Many factors can affect the effectiveness of the disinfection process. These include the microorganism being targeted, the organic and inorganic load present, the characteristics of the disinfectant (or disinfectant method) being used, as well as other factors such as temperature, pH, water hardness, relative humidity, and the physical nature of the object or surface being disinfected. For the use of physical disinfection methods, including heat, there are likely to be specific requirements and processes based on the situation and/or the disease agent involved.